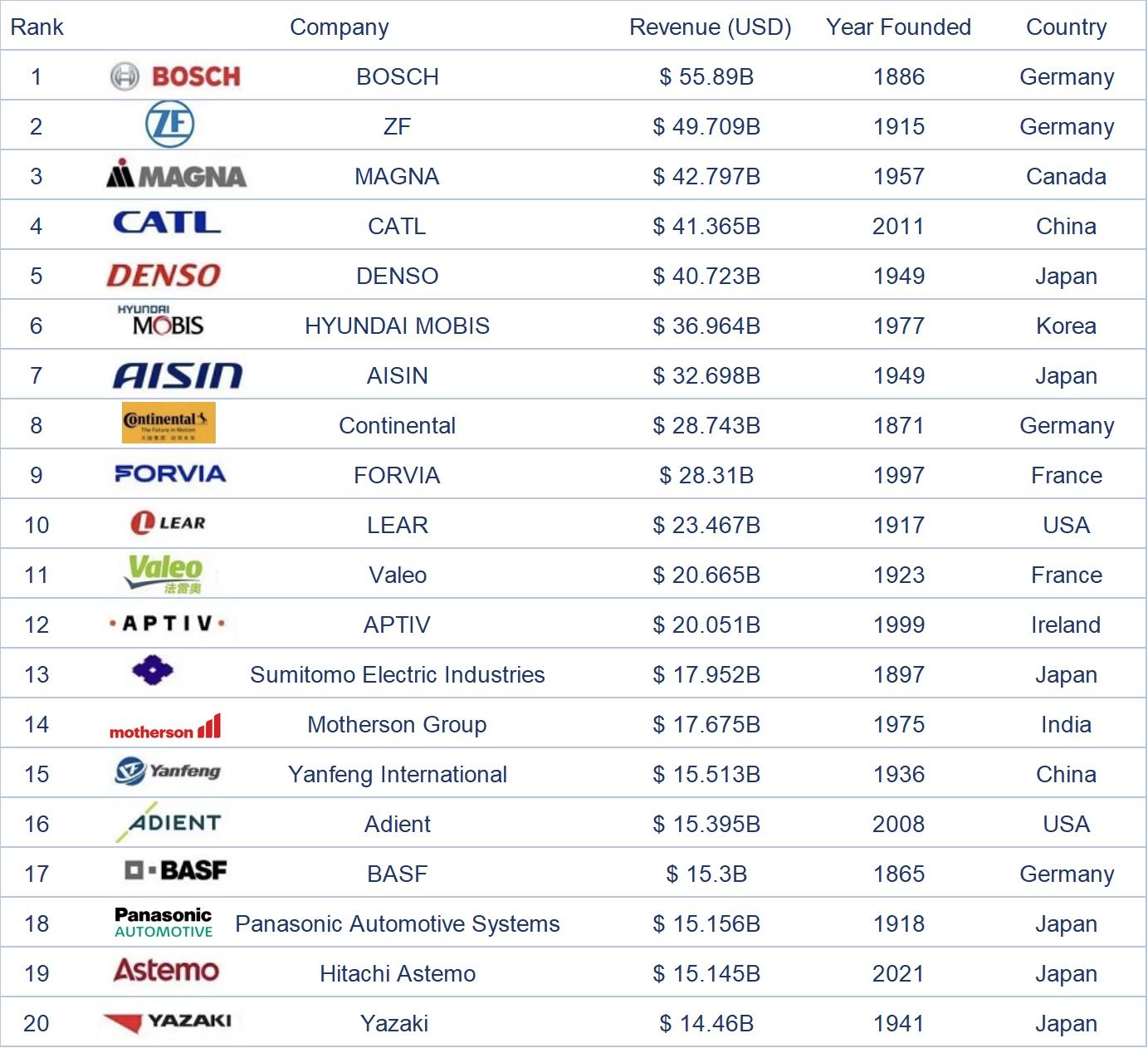
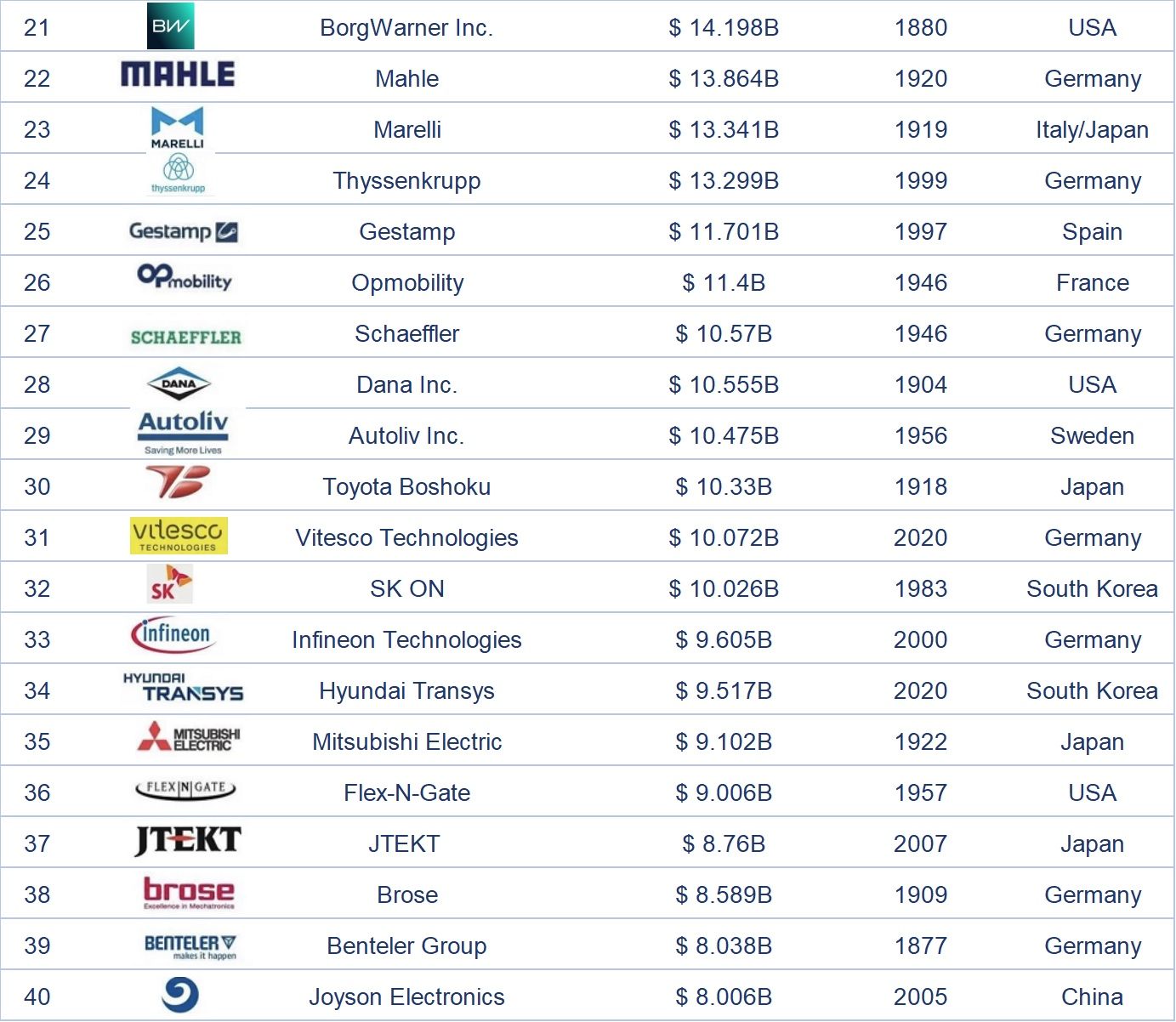
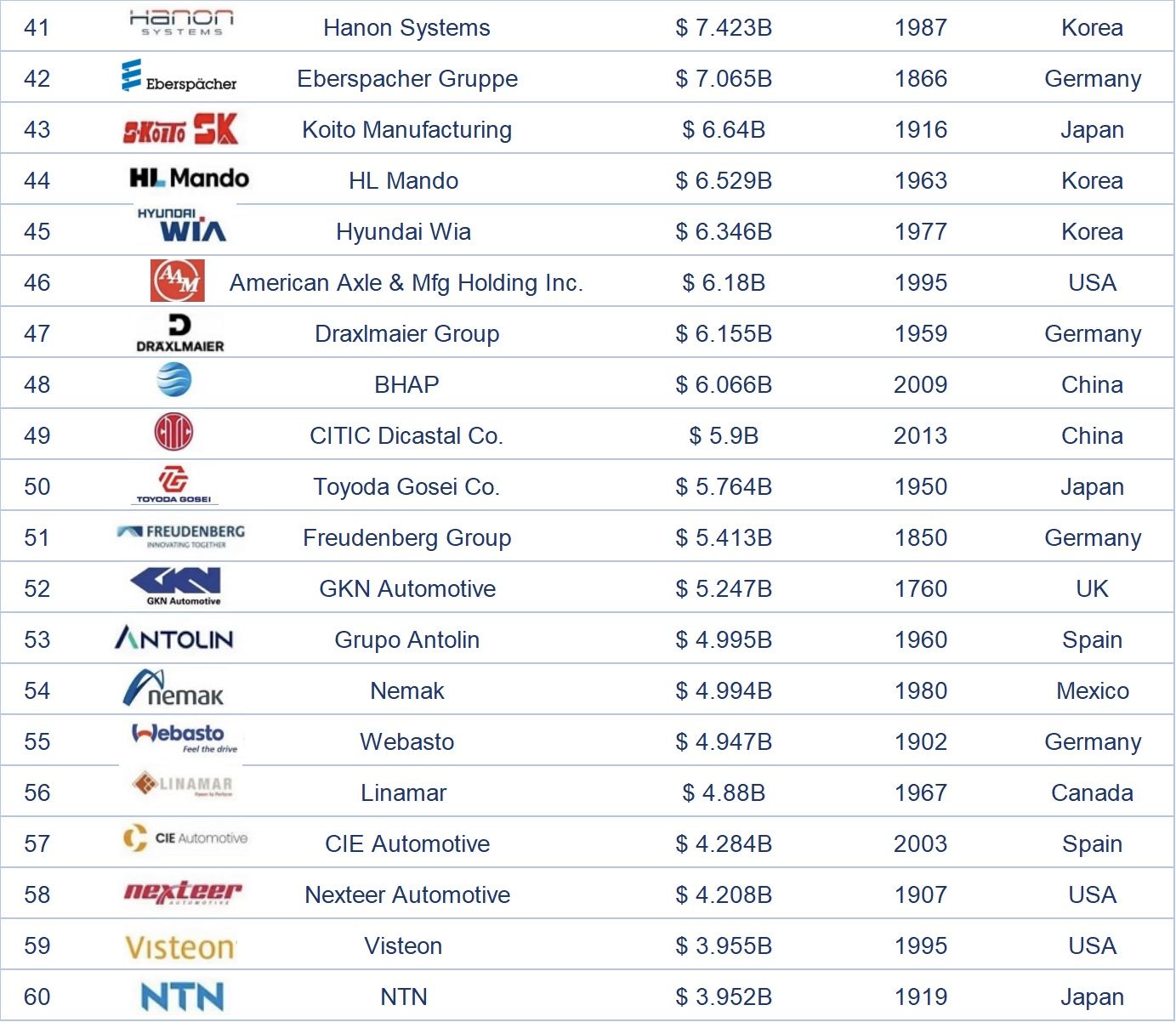
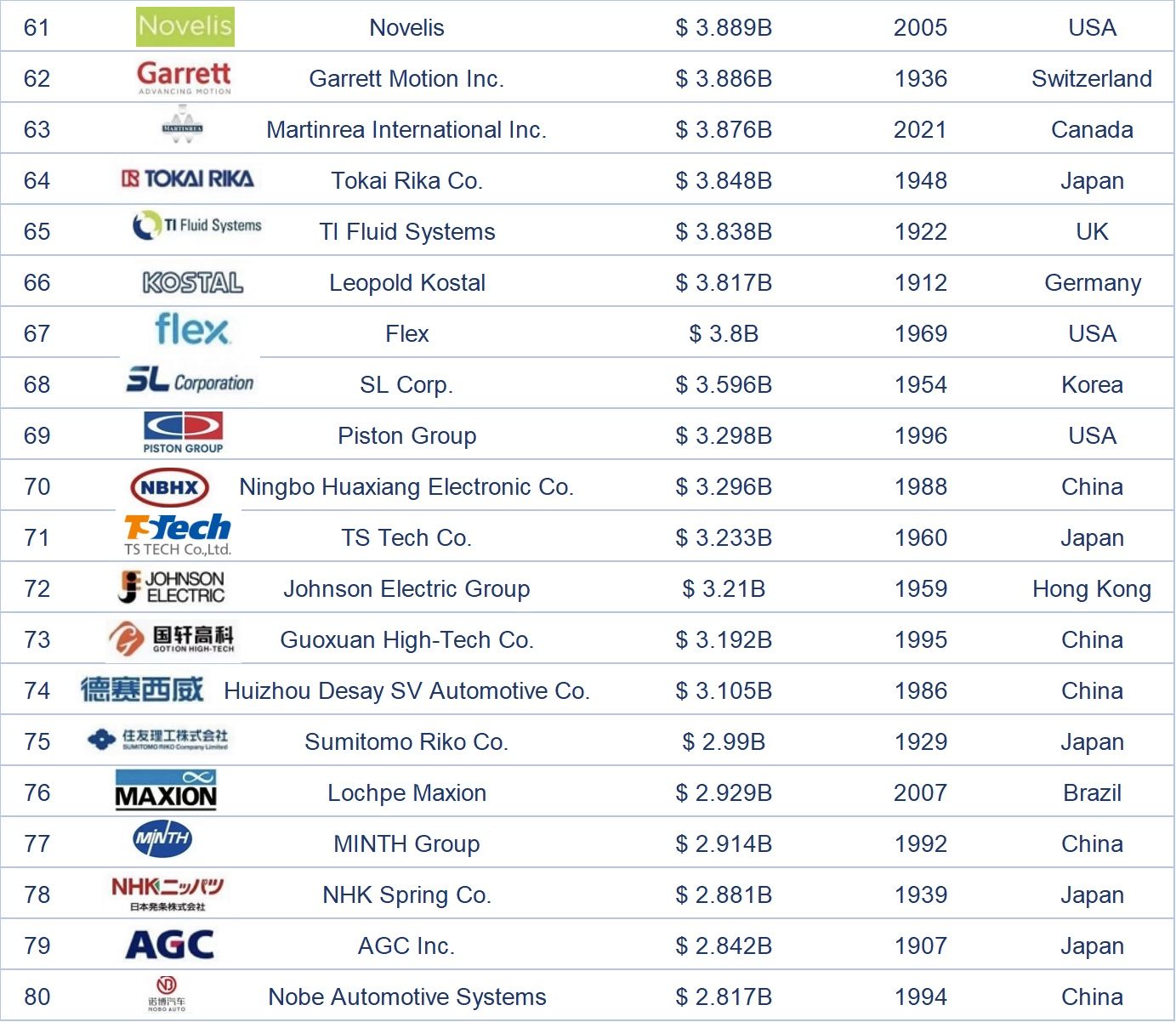
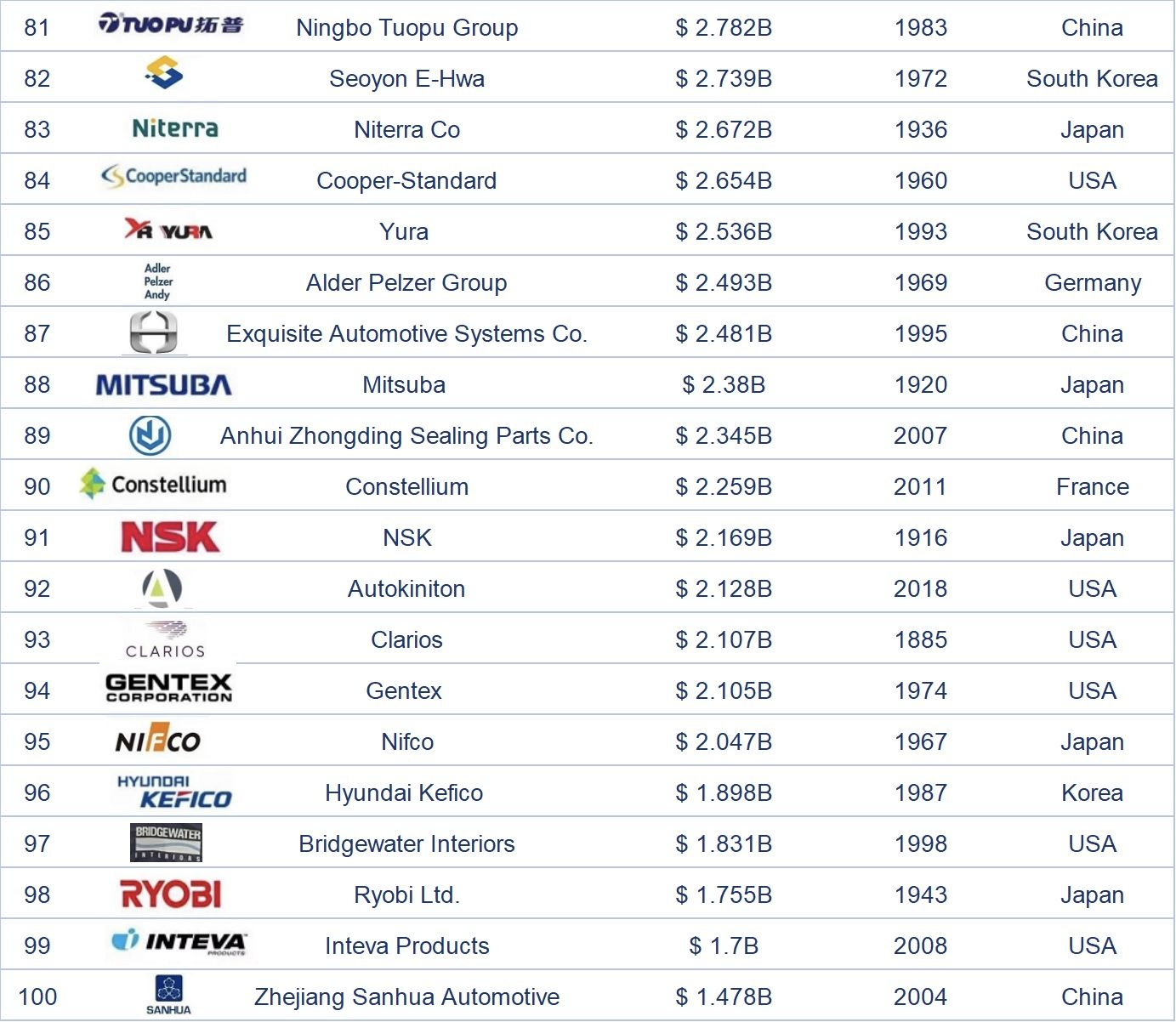
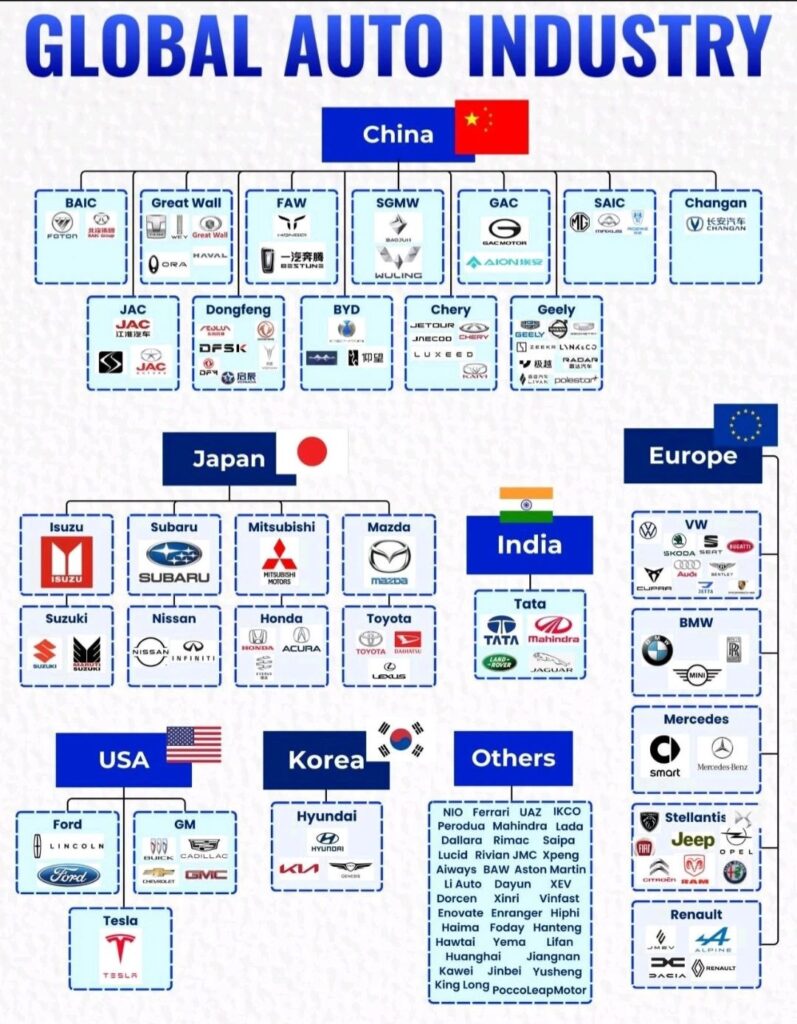
Dalam senarai 100 pembekal bahagian automotif global teratas pada tahun 2024, syarikat-syarikat Jepun mempunyai bilangan yang paling banyak, iaitu 22, dan merupakan satu-satunya negara yang mempunyai lebih daripada 20 syarikat. Terdapat 15 syarikat China dalam senarai ini, kedua terbanyak selepas Jepun, Amerika Syarikat, dan Jerman. Negara-negara yang mempunyai sepuluh atau lebih syarikat termasuk Korea Selatan, yang mempunyai 10 syarikat dalam senarai ini. Lebih daripada 80% daripada 100 pembekal bahagian automotif global teratas pada tahun 2024 tertumpu di lima negara teratas.
Keberhasilan ini bergantung pada pengeluar kereta OEM di negara-negara tempatan, jadi pendapatan dan aspek lain jauh melebihi pembekal utama di negara-negara lain. Khususnya, CATL, sebagai satu-satunya syarikat China dalam 10 teratas, bergantung pada penjualan kenderaan elektrik di tanah besar China dan juga menunjukkan kemajuan pesat China dalam bidang bahagian kenderaan elektrik.
Semasa menyusun senarai ini, saya juga membandingkan data untuk tahun 2022 dan 2023. Hampir 90% syarikat mengalami peningkatan pendapatan yang ketara, yang mencerminkan peningkatan dalam kapasiti penghantaran pengeluaran pembekal setelah mengalami era kekurangan semikonduktor, walaupun jualan kereta global lebih rendah daripada anggaran mereka. Walau bagaimanapun, kesan terhadap pendapatan kebanyakan pembekal utama adalah agak kecil. Saya percaya bahawa beberapa syarikat akan menunjukkan semangat sekali lagi setelah menyesuaikan strategi mereka dan menyelesaikan beberapa masalah dalam rantaian modal dan bekalan.
Nota: Kedudukan di atas disusun berdasarkan berita automotif dan laporan industri yang berkaitan.
The issue described suggests that a supplier may only provide components to local brand manufacturers, potentially adhering to different standards despite meeting automotive specifications. This could create challenges for global or non-local brands that require consistent quality and standards across their supply chain. Here are some potential solutions:
1. Clarify and Align Standards.
– Engage in Dialogue: Initiate discussions with the supplier to understand their standards and clarify your requirements. Ensure they can meet the specific automotive standards your company requires.
– Certifications: Request certifications or documentation proving their compliance with international or specific automotive standards (e.g., ISO/TS 16949, IATF 16949).
2. Diversify Suppliers
– Identify Alternative Suppliers: Look for other suppliers who can meet your standards and have experience working with global or non-local brands.
– Dual Sourcing: Consider dual sourcing to reduce dependency on a single supplier and ensure continuity of supply.
3. Conduct Audits and Quality Checks
– Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits to verify that the supplier’s processes and products meet your standards.
– Third-Party Inspections: Hire third-party inspectors to evaluate the supplier’s quality control processes and product conformity.
4. Collaborate on Improvement
– Technical Support:Offer technical assistance or training to help the supplier align with your standards.
– Joint Development: Work together to develop processes or products that meet both local and international requirements.
5. Contractual Agreements
– Clear Specifications: Include detailed technical specifications and quality requirements in the contract.
– Penalties for Non-Compliance:Establish penalties for failing to meet agreed-upon standards.
6. Leverage Local Partnerships
– Local Partnerships:Partner with local manufacturers or intermediaries who can bridge the gap between your standards and the supplier’s capabilities.
– Joint Ventures:Explore joint ventures or collaborations to ensure alignment with your standards.
7. Regulatory Compliance
– Understand Local Regulations: Ensure that the supplier’s standards comply with both local regulations and your company’s global requirements.
– Advocate for Harmonization: Work with industry groups to advocate for harmonized standards across regions.
8. Risk Mitigation
– Risk Assessment:Conduct a risk assessment to evaluate the impact of potential quality issues and develop mitigation strategies.
– Contingency Plans: Develop contingency plans in case the supplier fails to meet your standards.
By addressing the issue proactively and collaboratively, you can ensure that the supplier meets your standards while maintaining a strong and reliable supply chain.